模板编译
模板编译入口在$mount中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
const mount = Vue.prototype.$mount
Vue.prototype.$mount = function (
el?: string | Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
el = el && query(el)
const options = this.$options
if (!options.render) {
let template = options.template
if (template) {
if (typeof template === 'string') {
if (template.charAt(0) === '#') {
template = idToTemplate(template)
}
} else if (template.nodeType) {
template = template.innerHTML
} else {
return this
}
} else if (el) {
template = getOuterHTML(el)
}
if (template) {
const { render, staticRenderFns } = compileToFunctions(template, {
shouldDecodeNewlines,
shouldDecodeNewlinesForHref,
delimiters: options.delimiters,
comments: options.comments
}, this)
options.render = render
options.staticRenderFns = staticRenderFns
}
}
return mount.call(this, el, hydrating)
}
|
代码中可以看出编译模板之后才执行原来的$mount方法
接着看 compileToFunctions 函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
import { baseOptions } from './options'
import { createCompiler } from 'compiler/index'
const { compile, compileToFunctions } = createCompiler(baseOptions)
export { compile, compileToFunctions }
|
顺着 createCompiler 接着找
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
import { parse } from './parser/index'
import { optimize } from './optimizer'
import { generate } from './codegen/index'
import { createCompilerCreator } from './create-compiler'
export const createCompiler = createCompilerCreator(function baseCompile (
template: string,
options: CompilerOptions
): CompiledResult {
const ast = parse(template.trim(), options)
if (options.optimize !== false) {
optimize(ast, options)
}
const code = generate(ast, options)
return {
ast,
render: code.render,
staticRenderFns: code.staticRenderFns
}
})
|
createCompilerCreator
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
import { extend } from 'shared/util'
import { detectErrors } from './error-detector'
import { createCompileToFunctionFn } from './to-function'
export function createCompilerCreator (baseCompile: Function): Function {
return function createCompiler (baseOptions: CompilerOptions) {
function compile (
template: string,
options?: CompilerOptions
): CompiledResult {
...
const compiled = baseCompile(template.trim(), finalOptions)
return compiled
}
return {
compile,
compileToFunctions: createCompileToFunctionFn(compile)
}
}
}
|
千辛万苦终于拿到render函数,这里之所以那么绕时因为在不同平台下都会有编译过程,编译过程中的 baseOptions 会有所不同,而编译过程会多次执行,但是在同一平台下的编译配置优势相同的,为了不让这些配置在每次编译过程中通过参数传入,这里使用了柯里化计数实现了baseOptions的保留,通过createCompilerCreator(baseCompile) 的方法把真正的编译过程和其他逻辑剥离开。
编译的入口其实为
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| export const createCompiler = createCompilerCreator(function baseCompile (
template: string,
options: CompilerOptions
): CompiledResult {
const ast = parse(template.trim(), options)
if (options.optimize !== false) {
optimize(ast, options)
}
const code = generate(ast, options)
return {
ast,
render: code.render,
staticRenderFns: code.staticRenderFns
}
})
|
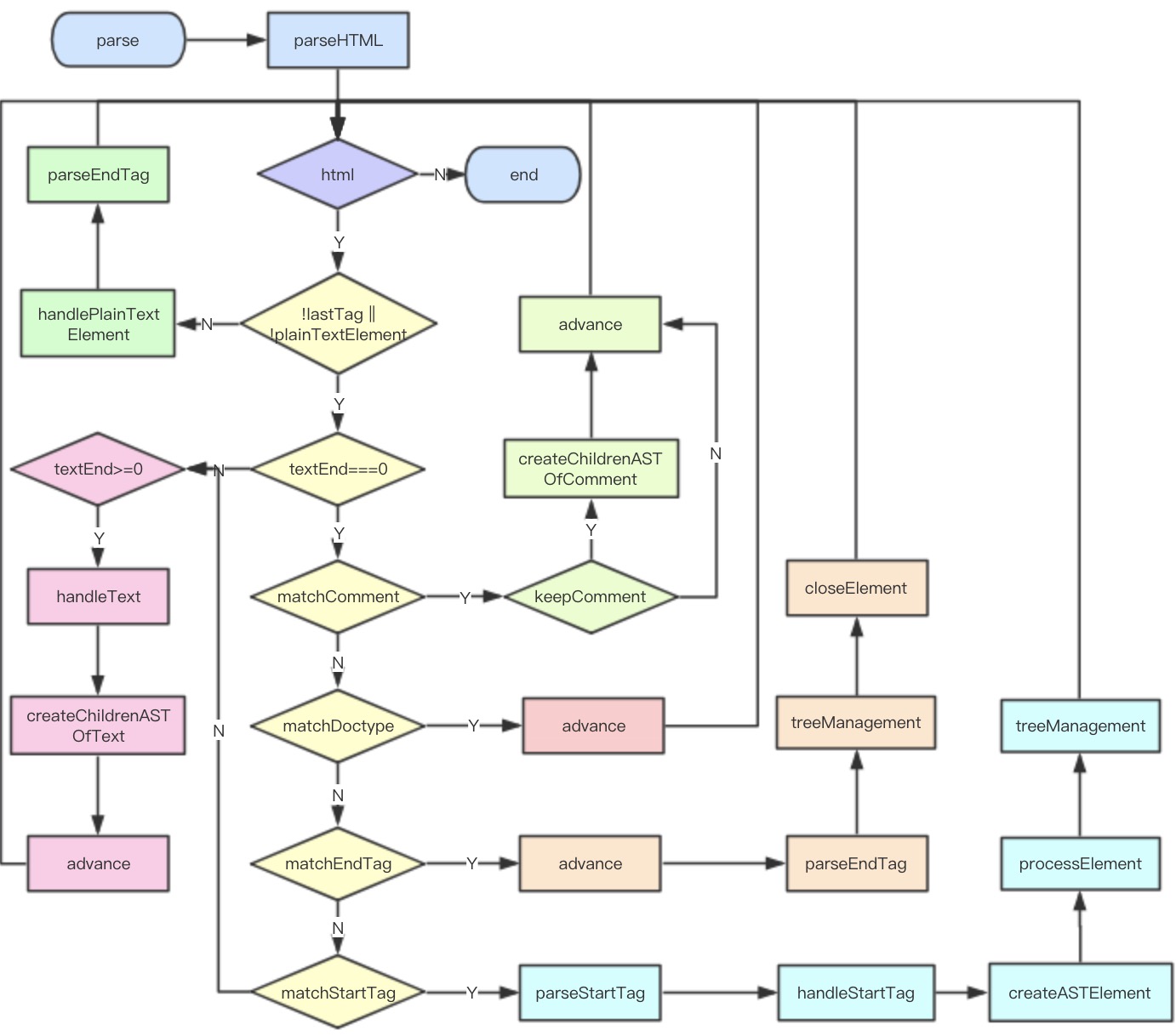
parse 生成AST
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
export function parse (
template: string,
options: CompilerOptions
): ASTElement | void {
...
const stack = []
let root
parseHTML(template, {
start (tag, attrs, unary, start, end) {
},
end (tag, start, end) {
},
chars (text: string, start: number, end: number) {
},
comment (text: string, start, end) {
}
})
return root
}
|

optimize
模板生成为AST树后,会对树进行优化。主要是对于一些首次渲染后不会再变化的数据可以在patch中跳过比对
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
export function optimize (root: ?ASTElement, options: CompilerOptions) {
if (!root) return
isStaticKey = genStaticKeysCached(options.staticKeys || '')
isPlatformReservedTag = options.isReservedTag || no
markStatic(root)
markStaticRoots(root, false)
}
|
整个 AST 树中的每一个元素节点标记了 static 和 staticRoot
generate
codegen 是一个有限自动机DFA,他会从一个状态开始,根据条件向下一个状态转移。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
| export function generate (
ast: ASTElement | void,
options: CompilerOptions
): CodegenResult {
const state = new CodegenState(options)
const code = ast ? (ast.tag === 'script' ? 'null' : genElement(ast, state)) : '_c("div")'
return {
render: `with(this){return ${code}}`,
staticRenderFns: state.staticRenderFns
}
}
export function genElement (el: ASTElement, state: CodegenState): string {
if (el.parent) {
el.pre = el.pre || el.parent.pre
}
if (el.staticRoot && !el.staticProcessed) {
return genStatic(el, state)
} else if (el.once && !el.onceProcessed) {
return genOnce(el, state)
} else if (el.for && !el.forProcessed) {
return genFor(el, state)
} else if (el.if && !el.ifProcessed) {
return genIf(el, state)
} else if (el.tag === 'template' && !el.slotTarget && !state.pre) {
return genChildren(el, state) || 'void 0'
} else if (el.tag === 'slot') {
return genSlot(el, state)
} else {
let code
if (el.component) {
code = genComponent(el.component, el, state)
} else {
let data
if (!el.plain || (el.pre && state.maybeComponent(el))) {
data = genData(el, state)
}
const children = el.inlineTemplate ? null : genChildren(el, state, true)
code = `_c('${el.tag}'${
data ? `,${data}` : '' // data
}${
children ? `,${children}` : '' // children
})`
}
for (let i = 0; i < state.transforms.length; i++) {
code = state.transforms[i](el, code)
}
return code
}
}
|