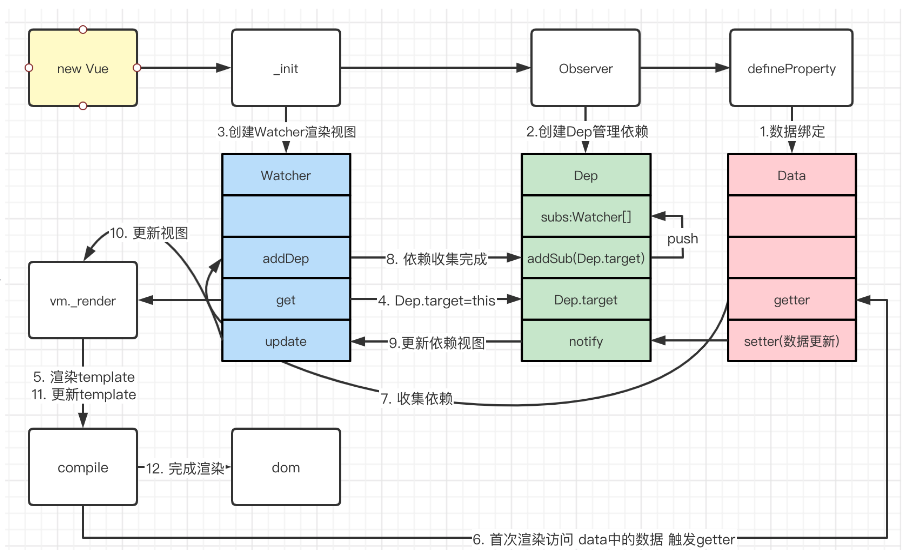
手写响应式原理
根据之前整理的流程

使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| ...
<div id="app">
</div>
<input type="text" name="" id="value">
<br>
<button id="push">push</button>
<button id="pop">pop</button>
<script type="module" src="/main.js"></script>
...
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| import MyVue from './source/MyVue'
const vm = window.vm = new MyVue({
el: '#app',
template: `
<p>name: {{name}}</p>
<p>name: {{computedName}}</p>
<p>name: {{watchName}}</p>
<p>inner.name: {{inner.name}}</p>
<p>dataList[0].name: {{dataList[0].name}}</p>
<p>list: {{list.join(',')}}</p>
`,
data(){
return {
name: 'xy',
inner: {
name: 'inner-xy'
},
list: [0, 1],
dataList: [{ name: 'deep-xy'}],
watchName: '2',
}
},
computed: {
computedName(){
return `computed ${this.name} ${this.name}`
}
},
watch:{
name(val){
this.watchName = `watch ${val}`
console.log(this);
}
}
});
document.getElementById('value').addEventListener('input', (e) => {
const value = e.target.value
vm.name = vm.inner.name = vm.dataList[0].name = value
})
document.getElementById('push').addEventListener('click', () => {
vm.list.push(vm.list.length)
})
document.getElementById('pop').addEventListener('click', () => {
vm.list.pop()
})
|
Vue 类入口
书写方法并且暴露出去,这里预计实现state、computed、watch 功能
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| export default function MyVue(options){
const vm = this.vm = this
vm.$options = options
initState(vm)
initComputed(vm)
initWatch(vm)
if(vm.$options.el){
vm.$mount()
}
}
|
接下来实现 initState
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
function initState(vm){
const fn = vm.$options.data
const data = vm._data = getData(fn, vm)
for (const key of Object.keys(data)) {
proxy(vm, '_data', key)
}
observe(data)
return vm
function getData(data, vm){
if(typeof data !== 'function') return {}
pushTarget()
try {
return data.call(vm, vm)
} catch (error) {
console.log(error)
} finally {
popTarget()
}
}
function proxy(target, sourceKey, key){
Object.defineProperty(target, key, {
get(){
return this[sourceKey][key]
},
set(val){
this[sourceKey][key] = val
},
enumerable: true,
configurable: true
})
}
}
|
这段代码最核心的部分是 observe(data)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
|
import { Dep } from './Dep';
import { arrayMethods, dependArray } from './Array';
export function observe(value){
if(!value || typeof value !== 'object' || value.__ob__) return
let ob = new Observer(value);
return ob
}
export class Observer{
constructor(value){
this.value = value
this.dep = new Dep()
Object.defineProperty(value, '__ob__', {
value: this,
enumerable: false,
writable: true,
configurable: true
})
if(Array.isArray(value)){
value.__proto__ = arrayMethods
this.observeArray(value)
}else{
this.walk(value)
}
}
walk(obj){
for (const [key, val] of Object.entries(obj)) {
defineReactive(obj, key, val)
}
}
observeArray (items) {
for (let i = 0, l = items.length; i < l; i++) {
observe(items[i])
}
}
}
export function defineReactive(obj, key, val){
const dep = new Dep()
let childOb = observe(val)
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get(){
if(Dep.target){
dep.depend()
if(childOb){
childOb.dep.depend();
if(Array.isArray(val)){
dependArray(val);
}
}
}
return val
},
set(newVal){
if(val === newVal) return
val = newVal
childOb = observe(newVal)
dep.notify()
}
})
}
|
这里面需要注意的是对数组的通知变化方式,是通过劫持原原型上方法实现的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
export const arrayMethods = Object.create(Array.prototype)
export const methods = ['push', 'shift', 'pop', 'unshift', 'reverse', 'sort', 'splice']
methods.forEach(method => {
arrayMethods[method] = function (...args) {
const res = Array.prototype[method].apply(this, args)
const ob = this.__ob__
let inserted
switch (method) {
case 'push':
case 'unshift':
inserted = args
break
case 'splice':
inserted = args.slice(2)
}
if(inserted) {
ob.observeArray(inserted)
}
ob.dep.notify()
return res
}
})
export function dependArray(value){
for (let i = 0; i < value.length; i++) {
const e = value[i];
if(e && e.__ob__ && e.__ob__.dep){
e.__ob__.dep.depend()
}
if(Array.isArray(e)){
dependArray(e)
}
}
}
|
Dep类实现了收集依赖和派发通知
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
let id = 0
export class Dep {
constructor(){
this.id = id++
this.subs = []
}
addSub(watcher){
this.subs.push(watcher)
}
removeSub(watcher){
this.subs = this.subs.filter(w => w !== watcher)
}
depend(){
if(Dep.target){
Dep.target.addDep(this)
}
}
notify(){
this.subs.forEach(sub => sub.update())
}
}
Dep.target = null
const stack = []
export function pushTarget(target){
stack.push(target)
Dep.target = target
}
export function popTarget(){
stack.pop()
Dep.target = stack[stack.length - 1]
}
|
接着来实现Watcher
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
| import { pushTarget, popTarget } from './Dep';
import { util } from './Compiler';
let id = 0
export class Watcher{
constructor(vm, expOrFn, cb, opts = {}) {
this.vm = vm
this.id = ++id
this.lazy = !!opts.lazy
this.dirty = this.lazy
this.cb = cb || (() => {})
this.getter = typeof expOrFn === 'function' ? expOrFn : () => {
return util.getValue(vm, expOrFn)
}
this.depIds = new Set()
this.newDepIds = new Set()
this.deps = []
this.newDeps = []
this.value = this.lazy ? undefined : this.get()
}
get(){
pushTarget(this)
let value
const vm = this.vm
try {
value = this.getter.call(vm, vm)
} catch (error) {
console.log(error)
} finally {
this.cleanupDeps()
popTarget()
}
return value
}
run(){
let value = this.get()
if(this.value !== value){
this.cb.call(this.vm, value, this.value)
this.value = value
}
}
addDep(dep){
let id = dep.id
if (!this.newDepIds.has(id)) {
this.newDepIds.add(id)
this.newDeps.push(dep)
if (!this.depIds.has(id)) {
dep.addSub(this)
}
}
}
update(){
if(this.lazy){
this.dirty = true
}else{
queueWatcher(this)
}
}
evalValue(){
this.value = this.get()
this.dirty = false
}
depend(){
let i = this.deps.length
while(i--){
this.deps[i].depend()
}
}
cleanupDeps () {
let i = this.deps.length
while (i--) {
const dep = this.deps[i]
if (!this.newDepIds.has(dep.id)) {
dep.removeSub(this)
}
}
let tmp = this.depIds
this.depIds = this.newDepIds
this.newDepIds = tmp
this.newDepIds.clear()
tmp = this.deps
this.deps = this.newDeps
this.newDeps = tmp
this.newDeps.length = 0
}
}
let has = {}
let queue = []
function queueWatcher(watcher){
let id = watcher.id
if(!has[id]){
has[id] = true
queue.push(watcher)
}
nextTick(flushQueue)
}
function flushQueue(){
for (let i = 0; i < queue.length; i++) {
let watcher = queue[i]
let id = watcher.id
has[id] = null
watcher.run()
}
queue = []
has = {}
}
let callbacks = []
function flushCallbacks(){
callbacks.forEach(cb => cb())
callbacks = []
}
function nextTick(flushQueue){
callbacks.push(flushQueue)
return Promise.resolve().then(flushCallbacks)
}
|
watcher 实例实在$mounted之前完成的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
MyVue.prototype.$mount = function(){
const vm = this
vm.$el = query(vm.$options.el)
new Watcher(vm, () => {
console.log('渲染')
vm._update()
})
return vm
function query(el) {
if (typeof el === 'string'){
return document.querySelector(el)
}
return el
}
}
MyVue.prototype._update = function(){
const vm = this
const el = vm.$el
el.innerHTML = compiler(vm)
}
const Reg = /\{\{((?:.|\r?\n)+?)\}\}/g
export const util = {
getValue(vm, exp){
let val
eval(`val = vm.${exp}`)
return val
},
compilerText(vm){
return vm.$options.template.replace(Reg, (...args) => {
return util.getValue(vm, args[1])
})
}
}
export function compiler(vm){
return util.compilerText(vm)
|
至此,响应式的原理已经写完了,接下去写computed的逻辑
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
function initComputed(vm){
const computed = vm.$options.computed || Object.create(null)
let watcher = vm._watcherComputed = Object.create(null)
for (const [key, userDef] of Object.entries(computed)) {
watcher[key] = new Watcher(vm, userDef, () => {}, { lazy: true })
Object.defineProperty(vm, key, {
get:((vm, key) => {
let watcher = vm._watcherComputed[key]
return function(){
if(watcher){
if(watcher.dirty){
watcher.evalValue()
}
if(Dep.target){
watcher.depend()
}
return watcher.value
}
}
})(vm, key)
})
}
}
|
最后把watch补完
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
MyVue.prototype.$watch = function(key, handler){
let vm = this
const watcher = new Watcher(vm, key, handler)
handler.call(vm, watcher.value);
return
}
function initWatch(vm){
const watch = vm.$options.watch || Object.create(null)
for (const [key, handler] of Object.entries(watch)){
vm.$watch(key, handler)
}
}
|